 I am reading stories right now for a teaching gig I have coming up in early March. I’ll be running a critique workshop, and so I not only have to read and comment on the manuscripts, I also should take the opportunity to turn the issues I identify into writing lessons. Because the truth is, all the submissions seem to be from writers with limited experience, and all the submissions suffer from similar problems.
I am reading stories right now for a teaching gig I have coming up in early March. I’ll be running a critique workshop, and so I not only have to read and comment on the manuscripts, I also should take the opportunity to turn the issues I identify into writing lessons. Because the truth is, all the submissions seem to be from writers with limited experience, and all the submissions suffer from similar problems.
Let me be clear: I’m not denigrating any of the writers in the group. The problems I’m seeing are ones that editors found in my work when I was starting out. I don’t make these errors as often now — I’ve moved on to new mistakes. And when I’ve overcome this new set of problems, I have no doubt that I will find still newer ways to mess things up. This is the creative process — there’s a reason why authors should never stop relying on editors.
Back to the workshop manuscripts… Here is what I’m seeing: All of the writers have terrific ideas. Their worlds and magic systems are fresh and innovative and exciting. And their characters are compelling as well. Some of the writers need to work on staying in tight point of view and injecting emotion into their stories, but even on these fronts they’re doing fairly well.
The flaws I’m finding in their work are largely mechanical. Their story telling is good, but their prose is getting in the way of their narratives. Specifically, I’m seeing three trends again and again.
1) They are trying to do too much with each sentence. There are places in a manuscript where it is perfectly appropriate to use compound sentences, phrasings that rely on the connection of several clauses in order to express complex emotions. There are places where short declaratives work better. (See what I did there?) I have noticed, however, not just with this batch of manuscripts, but in other settings, going back years, that beginning writers are drawn to the complexities of longer phrases. It’s almost as if they feel that writing shorter sentences will expose them as newbies.
This isn’t the case. As my wonderful, talented, and wise friend, Faith Hunter, has pointed out, syntax and phrasing is to the written story what soundtracks are to movies. When the action ramps up in a movie, the music grows taut, staccato. When the action ramps up in written stories, phrases should become shorter, punchier. Thoughts should be pared to the bone. And even when the action isn’t necessarily at a fever pitch, it is fine to rely on short declaratives as well as longer sentences. Short phrases punctuate key passages, drawing attention to important moments. They are an invaluable tool. (See? Did it again.)
2) A related point: Beginning authors, including those whose manuscripts I’m reading now, often tie themselves (and their prose) in knots seeking clever phrases. Again and again, in my margin notes, I have tried to remind them that simpler is usually better. This is not to say that every phrase needs to be simple, that every sentence should be short and to the point. Stories written that way would bore an audience — books would read like grade school primers, which we don’t want.
But sometimes it’s clear that a writer has decided on a certain construction for a sentence, and even after that structure has become unwieldy, they continue to batter the phrasing into submission. I know I’ve done it. I have a rhythm in mind, and I. Am. Going. To. Make. It. Work! The problem is, by the time I’m done, the sentence is a mess. This is a “kill your darlings” moment. You may love the concept you had for that phrasing, but if it has turned into a struggle for you as you write it, chances are your readers will struggle with it too. Simple is better. Simple works. Try a different approach to the sentence. Shorten it. Or better yet, divide it into two (or three) sentences. Your readers will thank you. Your editors will thank you. The beleaguered instructor reading your manuscript for a workshop will thank you.
3) Finally, I see a lot of writers trying to shoehorn into their scenes great swaths of world building information. They know better than to resort to full-blown data dumps, but they feel compelled to explain certain elements of their world in the moment, and they do so by overloading their sentences with background. The result, again, is sentences with too many clauses, too much information, and no flow.
In a sense this is a point of view issue. When characters are in the moment — whether they are deep in an important conversation, or facing an immediate threat to their own safety or that of people they care about — they are unlikely to pause to consider, say, the history of the city they’re in, or the anatomical differences between different species in the world.
It may be that this is important information. But writers need to ask themselves, “Is it crucial that my reader know all of this right now?” Chances are it’s not. If it is, anticipate that need and work at least some of the information in before the action heats up. Otherwise, save it for later. Either way, don’t try to heap all of the necessary info into a single serving, like an over-eager kid at an all-you-can-eat buffet. Doing so only confuses readers and leaves syntax in shambles.
Write with purpose. Strive for concision. Remember that, more often than not, simple is better.
And keep at it.










 For the Winds of the Forelands series (Rules of Ascension, Seeds of Betrayal, Bonds of Vengeance, Shapers of Darkness, Weavers of War) , I created what is without a doubt the most complex “calendar” I’ve ever undertaken for any project. For those of you not familiar with the world, I’ll give a very brief description. The world has two moons, Ilias and Panya, the Lovers, who chase each other across the sky. Each turn (month) has one night when both moons are full (the Night of Two Moons) and one night when both moons are dark (Pitch Night). Each turn is also named for a god or goddess, and so each Night of Two Moons and each Pitch Night has a special meaning.
For the Winds of the Forelands series (Rules of Ascension, Seeds of Betrayal, Bonds of Vengeance, Shapers of Darkness, Weavers of War) , I created what is without a doubt the most complex “calendar” I’ve ever undertaken for any project. For those of you not familiar with the world, I’ll give a very brief description. The world has two moons, Ilias and Panya, the Lovers, who chase each other across the sky. Each turn (month) has one night when both moons are full (the Night of Two Moons) and one night when both moons are dark (Pitch Night). Each turn is also named for a god or goddess, and so each Night of Two Moons and each Pitch Night has a special meaning. I did something similar for the Islevale Cycle novels (Time’s Children, Time’s Demon, Time’s Assassin). In this world there are two primary deities, Kheraya (female) and Sipar (male), and the calendar is structured around them. It begins with the spring equinox — Kheraya’s Emergence, a day and night of enhanced magickal power and sensuality. The spring months are known as Kheraya’s Stirring, Kheraya’s Waking, Kheraya’s Ascent. The summer solstice is called Kheraya Ascendent, a day of feasts, celebration, and gift-giving. This is followed by the hot months of summer: Kheraya’s Descent, Fading, and Settling.
I did something similar for the Islevale Cycle novels (Time’s Children, Time’s Demon, Time’s Assassin). In this world there are two primary deities, Kheraya (female) and Sipar (male), and the calendar is structured around them. It begins with the spring equinox — Kheraya’s Emergence, a day and night of enhanced magickal power and sensuality. The spring months are known as Kheraya’s Stirring, Kheraya’s Waking, Kheraya’s Ascent. The summer solstice is called Kheraya Ascendent, a day of feasts, celebration, and gift-giving. This is followed by the hot months of summer: Kheraya’s Descent, Fading, and Settling.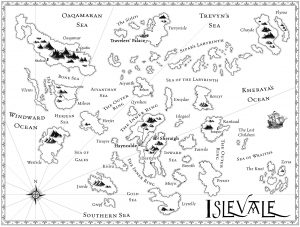 And then I just let my imagination run wild. At first I let my hand wander over the page, creating the broad outlines of my world. Sometimes I have to start over a couple of times before I come up with a design I like. But generally, I find that the less I impose pre-conceived notions on my world, the more successful my initial efforts. I draw land masses, taking care to make my shorelines realistically intricate. (Take a look at a map of the real world. Even seemingly “smooth” coastlines are actually filled with inlets, coves, islands, etc.) I put in rivers and lakes. I locate my mountain ranges, deserts, wetlands, etc.
And then I just let my imagination run wild. At first I let my hand wander over the page, creating the broad outlines of my world. Sometimes I have to start over a couple of times before I come up with a design I like. But generally, I find that the less I impose pre-conceived notions on my world, the more successful my initial efforts. I draw land masses, taking care to make my shorelines realistically intricate. (Take a look at a map of the real world. Even seemingly “smooth” coastlines are actually filled with inlets, coves, islands, etc.) I put in rivers and lakes. I locate my mountain ranges, deserts, wetlands, etc. When I finished writing the first draft of The Song of All, I was convinced of two things:
When I finished writing the first draft of The Song of All, I was convinced of two things: Over the next several months, as I edited The Song of All and honed my query letter, I felt confident saying, “The Song of All is a stand-alone epic fantasy novel with series potential.” After all, I had an outline, a roster of characters, and some heartfelt themes. I knew where the story was going and where it would end up. But when the series sold based on the first book and I began to write the second book, I soon realized that, while I had read tons of books in series, I had little or no idea of how to write one. In my giddy state as a writer with a book contract, I didn’t let this fact stop me. I continued to write the story, knowing that I would need to rewrite it many times, confident that I would learn how to write a series.
Over the next several months, as I edited The Song of All and honed my query letter, I felt confident saying, “The Song of All is a stand-alone epic fantasy novel with series potential.” After all, I had an outline, a roster of characters, and some heartfelt themes. I knew where the story was going and where it would end up. But when the series sold based on the first book and I began to write the second book, I soon realized that, while I had read tons of books in series, I had little or no idea of how to write one. In my giddy state as a writer with a book contract, I didn’t let this fact stop me. I continued to write the story, knowing that I would need to rewrite it many times, confident that I would learn how to write a series. 1. Fully explore and flesh out the world-building. For some writers of science fiction and fantasy this might be obvious because world-building is their jam, but for other writers, who are more interested in themes or characters or plot, digging deep into world building might not be their first choice. Nevertheless, the better your understanding of how your world works (geography, socio-economic and political structures, cultural and legal norms, clothing, food, relationships, architecture, magic, etc) the easier it will be to see how the plot will unfold, where the themes might manifest, and how the characters will react.
1. Fully explore and flesh out the world-building. For some writers of science fiction and fantasy this might be obvious because world-building is their jam, but for other writers, who are more interested in themes or characters or plot, digging deep into world building might not be their first choice. Nevertheless, the better your understanding of how your world works (geography, socio-economic and political structures, cultural and legal norms, clothing, food, relationships, architecture, magic, etc) the easier it will be to see how the plot will unfold, where the themes might manifest, and how the characters will react. 4. Upping the stakes without jumping the shark. What keeps someone reading a series? Characters we love (so develop those characters) and the situations they find themselves in. As a reader, I fall in love with characters and want to know what happens to them as they face challenges, but if they face the same challenges over and over it can get boring. I want them to learn and grow from their obstacles. As a writer, creating new challenges for growth can run the risk of going over the top. Killing off everyone that a character loves over a series definitely ups the stakes. But where does it leave your character? And where does it leave your reader? It is a balance between tension and emotional exhaustion, and something which I am still working on.
4. Upping the stakes without jumping the shark. What keeps someone reading a series? Characters we love (so develop those characters) and the situations they find themselves in. As a reader, I fall in love with characters and want to know what happens to them as they face challenges, but if they face the same challenges over and over it can get boring. I want them to learn and grow from their obstacles. As a writer, creating new challenges for growth can run the risk of going over the top. Killing off everyone that a character loves over a series definitely ups the stakes. But where does it leave your character? And where does it leave your reader? It is a balance between tension and emotional exhaustion, and something which I am still working on.
